By Suhani Chitalia, Manager, Environmental Regulatory Affairs and Kelly Scanlon, Director, Environmental Policy & Research
Leading companies in the electronics manufacturing industry are highly intentional about their environmental, social and governance (ESG) priorities, with climate change and energy use among the most closely scrutinized issues, an IPC analysis shows.
ESG reporting has gained significant momentum over the past few decades, ever since “sustainable development” became a global buzzword around the time of the 1992 Earth Summit. ESG reports, sometimes also identified as “Sustainability Reports,” are published by many companies and other kinds of organizations to share their priorities, metrics, and performance data with the public. ESG ratings can influence the financial services industry’s investment decisions about a company based on evidence that high-performing companies are safer long-term bets.
As the broad topic of sustainability continues to receive attention across the electronics industry, it will be important to know what aspects of sustainability are being prioritized by companies in the electronics value chain and why.
As part of IPC’s ESG for Electronics initiative, IPC is interested in developing resources for members on the most common ESG methods and priorities of leading companies across the electronics value chain. In support of this, IPC has preliminarily analyzed the ESG reports of approximately a dozen companies in selected portions of the industry.
IPC first wanted to understand whether ESG reporting is common within electronic companies and what priority areas electronics companies are being focused on. We selected just over a dozen companies for our initial, preliminary survey based on those with the highest revenues. The survey included companies in the wire/cable, EMS, OEM, and PCB sub-sectors. Our three main questions when surveying companies’ initiatives were:
- Whether the company had a sustainability or ESG report;
- What methodologies are used in determining which priorities are most "material” to the companies; and
- What are the most common company priorities?
Most companies in our preliminary survey were found to have published an ESG report on an annual or regular basis. Many companies used a materiality assessment to determine what priorities the company should focus in on in their ESG goals and reporting. Priority initiatives varied from company to company.
Ambitious Methodologies
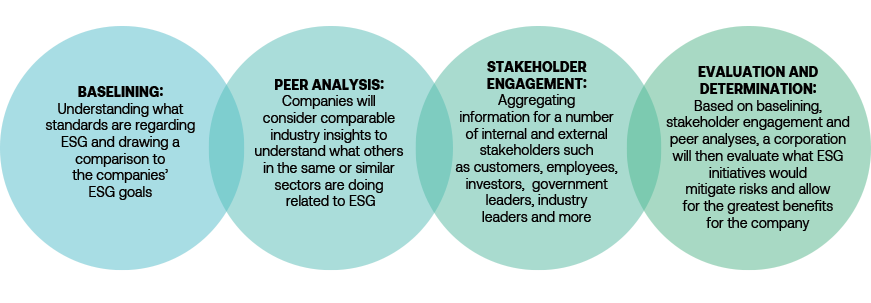
The methodology most used for determining a company’s ESG priorities is a materiality assessment, although the details of such assessments vary. A materiality assessment is designed to help companies identify and understand the relative importance of specific ESG and sustainability topics. All the electronics companies surveyed were very intentional with their priorities, as reflected by the ambitious processes involved.
Generally, the processes used included:
- Baselining
- Peer Analysis
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Evaluation and Determination
Baselining to Start
Zeroing in on baselining, this part of the process helps companies understand their status and what standards exist in the industry. Within baselining, we noticed two trends:
- Many companies hire consulting firms that have a specialty in ESG to conduct a materiality assessment. The consulting firm will engage with stakeholders, determine what issues are relevant to the company, and decide which issues should be prioritized for the companies and shareholders benefit most.
- Baselining can stem from existing standards created by national and global organizations. From our limited survey of electronics industry companies, most of them referred to the ESG standards from the following organizations:
Material Issues
Material issues are those that are likely to have the most “material impact” on the company’s revenues, profitability, and sustainability. Material issues are often determined in terms of the expectations and concerns of stakeholders, key financial risks, and legislative and regulatory frameworks. Across the electronics industry, we noticed several broad, overarching material issues including:
- Climate Change and Sustainable Development
- Financial Performance
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Supply Chain and Labor Standards/ Social Human Rights
- Ethical Governance
Climate Change a Common Focus
While many material issues identified by companies are broadly defined, some of the sub-categories are more closely scrutinized, especially greenhouse gas emission reduction, energy use, and water use.
For example, under the broad heading of climate change, several companies focused on greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction. GHG reduction goals have generally resulted in a focus on high-efficiency technologies; carbon-neutral production; an increased use of renewable energy sources; and working towards a circular economy. One company conducted a baseline analysis to understand where GHG emissions are high in their supply chain, and what measures are feasible to reduce them. Data showed that mechanical systems like air conditioning, air compression, and manufacturing utilized the highest rates of energy and were the areas offering the highest potential energy savings.
In addition to GHG reduction and climate change actions, many companies are also focusing on waste management and sustainable water management. For example, across this initial survey, many companies have prioritized reducing water usage and encouraging water recycling. One company used a Water Stress Index, which analyzes the water stress indicators of its global operations. With this data, the company can evaluate the risk ratings of various water resources and set up more efficient water management and water recycling equipment.
While the electronic industry continues to put in great efforts towards ESG accounting and disclosure, IPC wants to know where we can support our members on their ESG journey. ESG is becoming more prevalent in business practices, and as the association representing more than 3,000 electronics-related companies around the globe, we want to ensure that our members are up to speed on ESG policies and what others in the field are doing. Please contact either of us to discuss the types of resources that IPC can develop to benefit your company.