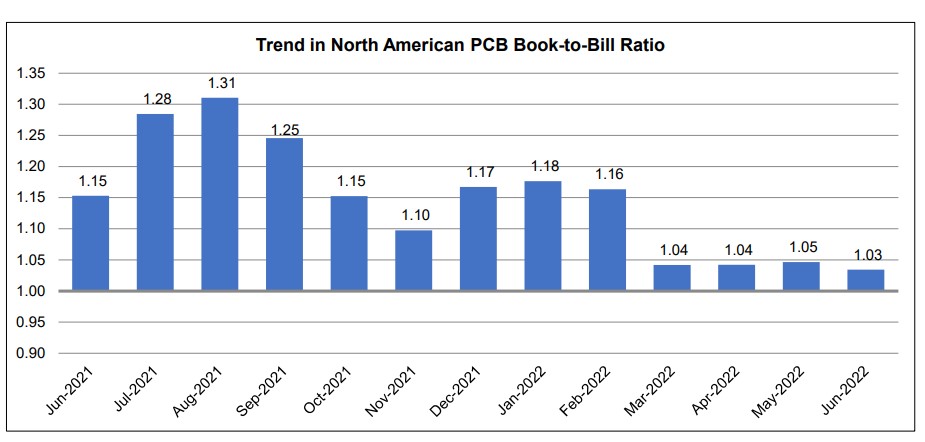
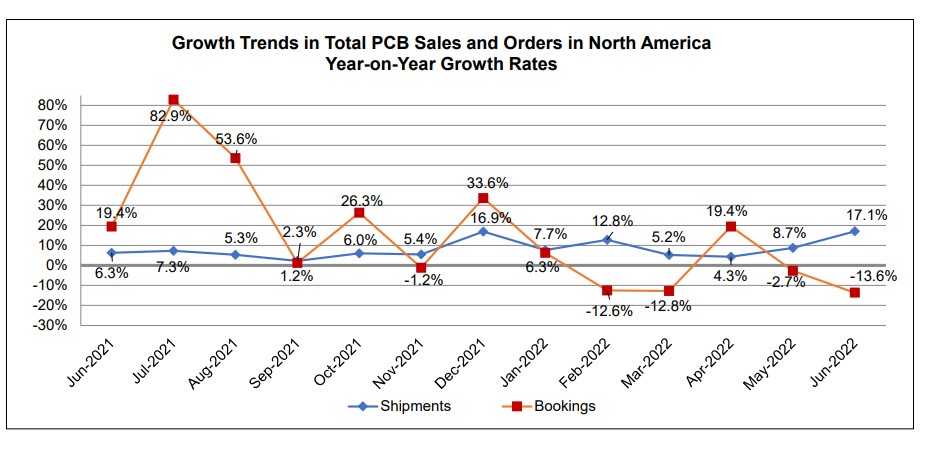
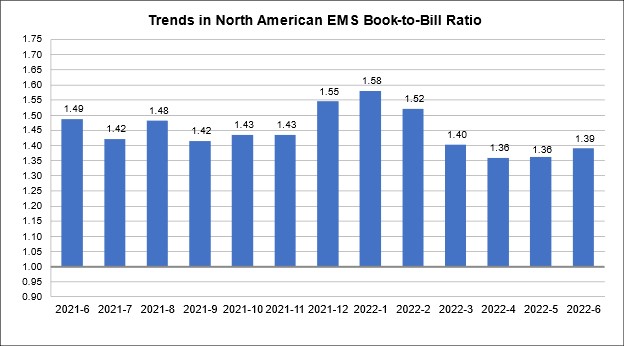
Microvia Reliability Testing Utilizing D-Coupons to Understand Best Design Practice
As Printed Circuit Board (PCB) designs increase in density, the need for High Density Interconnect (HDI) structures such as microvias is also increasing. With this uptick in microvia usage, there has also been an increase with reliability concerns. A structural weakness at the interface between the microvia target land and copper plating can occur eventually leading to a separation between the plating and the land. When bare boards are subjected to thermal cycling during reflow assembly, the microvias are susceptible to thermomechanical damage, causing intermittent circuit opens, leading to failures during Environmental Stress Screening (ESS) testing. These failures show the potential for latent defects that should they escape could potentially result in field failures. This reliability concern, including test failures, is well documented in the industry through reports from other Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), an IPC white paper released in 2018 [1,2], and from within all Business Areas of Lockheed Martin (LM).
This paper discusses the design of a microvia test coupons panel, the testing of the coupons and results from the testing. The design of the coupons included a wide range of design practices to be examined, including a variation in diameter of laser formed microvias, microvia aspect ratio, offset for microvia-to-microvia transitions, offset for microvia to mechanically drilled buried via transitions, number of via transitions in each coupon and the usage of copper planes in the coupons.
This effort was to identify a range of design parameters that lead to a higher probability of success when it comes to the reliability of microvias. There are also many contributing factors during manufacturing when it comes to creating reliable microvias, including many processing variables that interact with the designs. However, the focus of this study is on the influence of the design features.